Mendel's Experiment and his laws 1
In last Article we understood what is genetics and what are its applications , now let us study Mendelian genetics.i.e. the experiments carried out by Mendel and the laws proposed by him.
Gregor Johann Mendel
A priest and teacher from Brunn was sent to university of Vienna for higher studies in physics, mathematics and natural sciences. In 1856 he started his experiments on garden peas(Pisum sativum).
Unfortunately his work had remained unnoticed for many years till the findings were rediscovered by three scientists independently. They are-
1.Hugo De Vries from England
2.Karl Correns from Germany
3.Erich Tschermak from Austria
Based on Mendel's principle Correns postulated three laws which are known as Mendel's laws of inheritance.
Before studying Mendel's experiments let us get introduced to some important terms:
Character-It is a feature of an organism.Ex. Height, seed colour,etc.
Trait-An inherited character and its desirable variant.Ex Height character has two traits Tall and Dwarf.
Factor-It is a unit of heredity, a particle present in the organism which is responsible for he inheritance and expression of a character.(It is passed to next generation through gametes and not the character itself)
Gene-It is a particular segment of DNA which is responsible for expression and regulation of a particular character.(This term was coined by Johannsen)
Alleles or allelomorphs- The two or more alternative form of genes are called as alleles of each other.They occupy identical loci on homologous chromosomes.(This term was coined by bateson)
Homozygous-An individual possess in similar alleles for a particular trait is called as homozygous or pure for that trait.
Heterozygous-An individual possessing dissimilar alleles for a particular trait is called as heterozygous or hybrid for that trait.
Dominant-The allele that expresses itself even in the presence of an alternative allele.i.e. heterozygous condition.
Recessive-The allele that does not get expressed in the presence of another allele.i.e.Heterozygous condition.It gets expressed in homozygous condition.
Phenotype-The external appearance of an individual for any trait is called phenotype for that trait.
Genotype-The representation of the genetic constitution of an individual with respect to a single character or a set of characters is its genotype.
_________________________________________________________________________________
Let us see an Example:
If we have two alleles T(Dominant) for tall and t (Recessive) for dwarf , for the the height character.
A.Homozygous conditons:
In organism with genotype TT, T will be expressed and the plant will be tall.
In organism with Genotype tt, t will be expressed and plant will be dwarf.
B.Heterozygous condition:
In organism with Genotype Tt, T will be expressed and the plant will be tall(Here t is supressed by T)
_________________________________________________________________________________
Pure line-An individual or a group of individuals that is homozygous or true breeding for one or more traits.
Hybrid-It is a heterozygous individual produced from an cross involoving pure parents having one or more contrasting characters.
Monohybrid cross-It is a cross between two pure individuals(Parents) which are homozygous in which inheritance pattern of only one pair of contrasting characters is studied.
Dihybrid cross-It is a cross between two pure individuals(Parents) which are homozygous in which inheritance pattern of two pair of contrasting characters is studied simultaneously.
F1 generation-F stands for filial meaning offspring's produced in sexual reproduction.So, the progeny produced in a cross is called as first filial generation or F1 generation.It shows uniform expression.
F2 generation-The second generation produced by selfing of F1 generation offspring,s is called second filial generation or F2 generation.
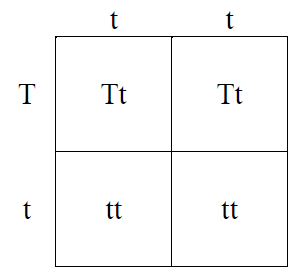
Punnet square-It is a diagram that is used to show possibilities of combinations in a particular cross or breeding experiment.
This is punnet square.
Why Mendel choose pea plants?
a.Its an annual plant and completes its life cycle within 3-4 months.
b.Due to this short life span he was able to grow three generations in a year.
c.It is a small herbaceous plant and produces many seeds so he could grow them in thousands in a small portion of land behind the church.
d.It is naturally self pollinating.
e.It is available in the form of many varieties with contrasting characters.
f.There were no intermediate characters.
g.Also the flowers were easy for emasculation.i.e. removal of anthers for artificial cross and produce fertile offspring's.
Which pairs of Contasting traits were considered and studied by Mendel?
There were seven pairs of contrasting traits studied by him as follows-
a.Its an annual plant and completes its life cycle within 3-4 months.
b.Due to this short life span he was able to grow three generations in a year.
c.It is a small herbaceous plant and produces many seeds so he could grow them in thousands in a small portion of land behind the church.
d.It is naturally self pollinating.
e.It is available in the form of many varieties with contrasting characters.
f.There were no intermediate characters.
g.Also the flowers were easy for emasculation.i.e. removal of anthers for artificial cross and produce fertile offspring's.
Which pairs of Contasting traits were considered and studied by Mendel?
There were seven pairs of contrasting traits studied by him as follows-


Comments
Post a Comment